Detection of Defect in Steel Sheets Under Coatings by Magnetic Flux Leakage
Published:
This project demonstrates the use of a portable magnetic flux leakage (MFL) setup built on STMicroelectronics’ SensorTile.box platform for detecting sub-coating defects in steel sheets. It shows how artificial gaps and different coatings affect flux leakage signals, validating the feasibility of low-cost embedded NDT.
Overview
This project explores the detection of defects in steel sheets covered with non-conducting coatings using the principle of Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL).
A compact setup based on STMicroelectronics SensorTile.box—which integrates the LIS2MDL 3-axis magnetometer—was developed to measure magnetic field variations caused by artificial defect gaps under coated surfaces.
By analyzing flux leakage signatures, the system demonstrates the feasibility of a portable, low-cost, and wireless NDT tool for industrial inspection.
Experimental Setup
The experimental setup employed neodymium magnets to magnetize the steel sheet. The SensorTile.box, containing the LIS2MDL magnetometer and STM32L4 microcontroller with Bluetooth connectivity, was positioned between the magnets to capture leakage fields. Data was transmitted wirelessly to a mobile device for real-time analysis.
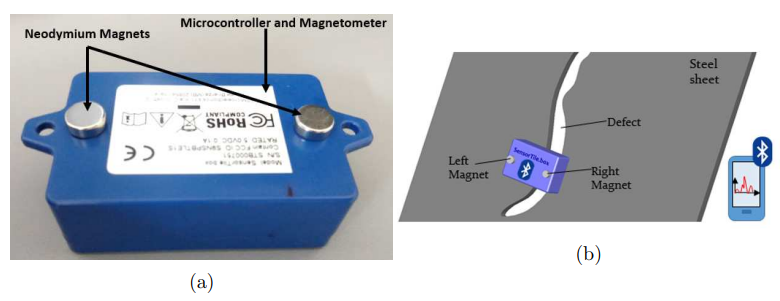
Figure 1: (a) SensorTile.box with neodymium magnets and embedded LIS2MDL. (b) Schematic of defect detection with magnetic flux leakage and Bluetooth readout.
The scanning process involved moving the sensor across the coated steel plate in a controlled direction.
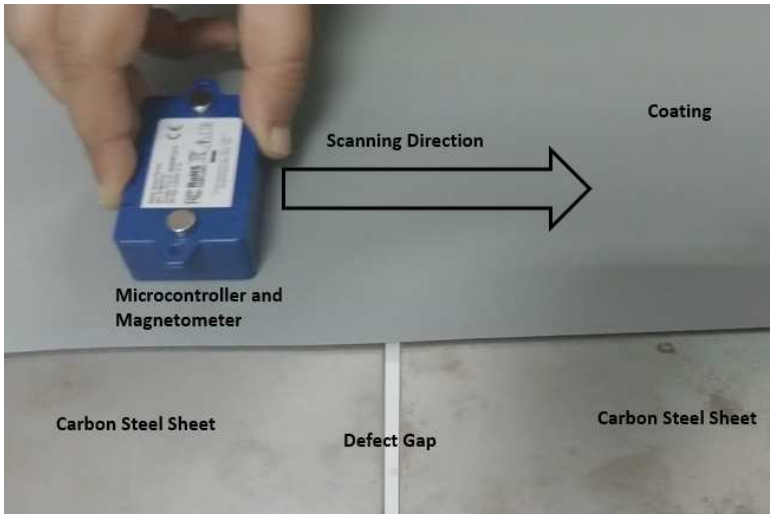
Figure 2: Scanning procedure across a coated carbon steel sheet with an artificial defect gap.
Defect Gap Analysis
Artificial gaps of varying sizes were introduced between two adjoining steel sheets to simulate defects. The response of the magnetometer was recorded under different conditions.

Figure 3: Test samples with no gap, 3 mm gap, and 6 mm gap.
The results showed a clear increase in magnetometer readings with larger gaps, indicating higher flux leakage.
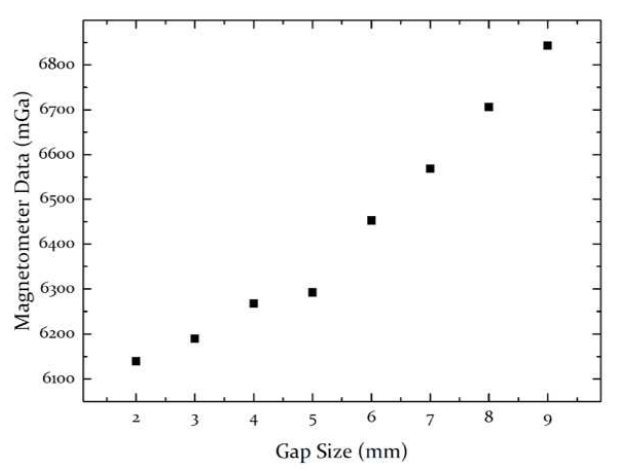
Figure 4: Relationship between defect gap size and measured magnetometer signal.
Influence of Coating Materials
To investigate the effect of coatings, different materials such as plywood, cardboard, paper, and rubber with varying thicknesses were placed above the defect region.

Figure 5: Magnetic flux leakage signals for plywood, rubber, and mixed stacks with different thicknesses.
The MFL method remained effective across different dielectric coatings, though the signal attenuation increased with coating thickness.

Figure 6: Magnetic flux leakage signals across different coating materials and thicknesses.
Additional Components
In this work, a sensitive magnetometer (LIS2MDL) is used, which comes built into the SensorTile.box platform.
- LIS2MDL: A 3-axis ultra-low-power magnetometer with ±50 gauss range, 16-bit resolution, and digital I²C/SPI output (STMicroelectronics, 2018).
- SensorTile.box (STEVAL-MKSBOX1V1): A wireless IoT and sensor kit featuring an STM32L4 MCU, Bluetooth connectivity, rechargeable battery, and multiple MEMS sensors including the LIS2MDL (STMicroelectronics, 2021).
Outcomes
- Developed a portable and wireless defect detection tool for steel sheets under coatings.
- Demonstrated that defect size strongly correlates with flux leakage signals, detectable even with coating layers.
- Validated that MFL can be adapted into a low-cost, embedded NDT method using commercial sensor platforms.
Key Learnings & Future Work
Key Learnings
- Gained hands-on experience in non-destructive testing (NDT) using magnetic flux leakage.
- Worked with embedded sensor platforms (STM32 + LIS2MDL) and Bluetooth-based data acquisition.
- Understood the influence of coating materials on detection sensitivity.
- Developed skills in signal analysis, experimental design, and interpretation of MFL data.
Future Work
- Extend testing to real industrial coatings (paints, epoxy layers) instead of lab substitutes.
- Improve system sensitivity by integrating higher resolution magnetometers and adaptive signal processing.
- Miniaturize the device further for field-deployable inspection kits.
- Explore machine learning approaches for automated defect classification.
Citation
Tamhane, D. Detection of Defect in Steel Sheets Under Coatings by Magnetic Flux Leakage. Available at: https://durgeshtamhane.github.io/projects/mfl-steel-under-coatings/.
BibTeX
```bibtex @misc{tamhane2023mfl, author = {Tamhane, Durgesh}, title = {Detection of Defect in Steel Sheets Under Coatings by Magnetic Flux Leakage}, year = {2023}, howpublished = {Term project report for the course CE 720: Non-Destructive Testing of Materials, IIT Bombay}, url = {https://durgeshtamhane.github.io/projects/mfl-steel-under-coatings/} }
